Vaccination
Home / Pediatrician / Vaccination
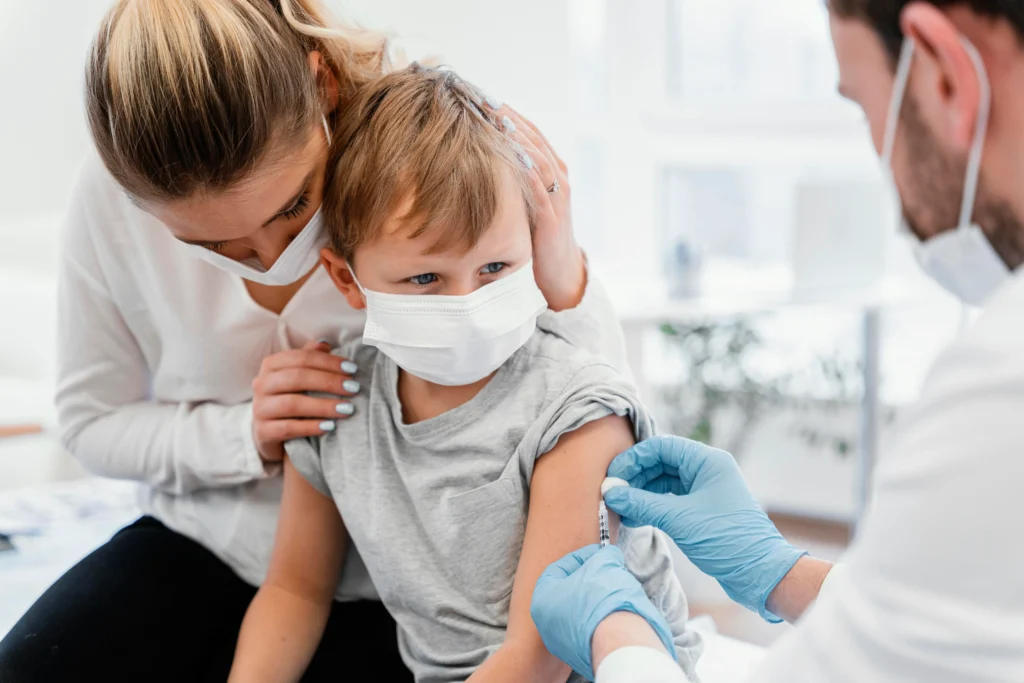
Understanding Vaccination
Vaccination is one of the most effective public health interventions in modern medicine. It involves the administration of a vaccine to stimulate an individual’s immune system to develop adaptive immunity to a pathogen. Vaccines have significantly reduced the prevalence of diseases such as measles, polio, and influenza, saving countless lives globally.
How Vaccines Work
Vaccines contain weakened or inactivated parts of a particular organism (antigen) that triggers an immune response within the body. Newer vaccines contain the blueprint for producing antigens rather than the antigen itself. This immune response allows the body to “remember” the pathogen and fight it more effectively if exposed to it in the future.
Benefits of Vaccination
Prevention of Diseases: Vaccination helps prevent the spread of infectious diseases. When a person is vaccinated, they are less likely to contract and spread the disease to others.
Herd Immunity: When a significant portion of the population is vaccinated, herd immunity is achieved. This provides indirect protection to those who are not immune, such as individuals who cannot be vaccinated due to medical conditions.
Eradication of Diseases: Successful vaccination campaigns have led to the eradication or near-eradication of certain diseases. Smallpox is a prime example, having been declared eradicated in 1980 due to widespread vaccination efforts.



